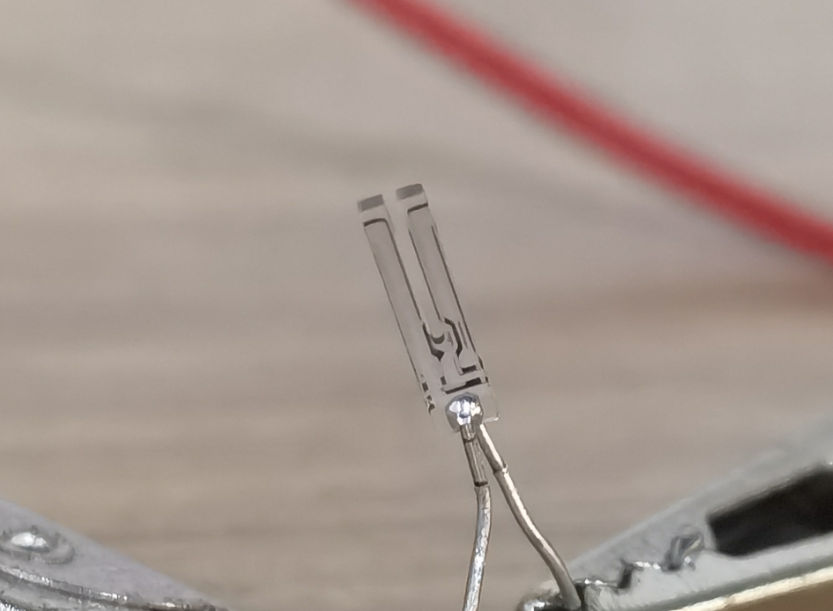
The tuning fork crystal as it is used in watches is something like the “classic” among the quartz crystals. Its frequency is always exactly 32.768 kHz. But why this value?
手表中使用的音叉水晶有点像石英水晶中的“经典”。它的频率始终恰好是 32.768 kHz。但为什么会是这个数值呢?
The answer to this question can be found in the history of quartz crystals. Bell Telephone Laboratories, the former research department of today’s telecommunications group AT&T, is one of the pioneers in this field. Initially, their research focused on stabilizing radio frequencies, but it soon became clear that quartz crystals are also useful for time measurement. In 1928, the Americans proudly presented the world’s first quartz-controlled Clock.
这个问题的答案可以在石英晶体的历史中找到。贝尔电话实验室是当今电信集团 AT&T 的前研究部门,是该领域的先驱之一。最初,他们的研究重点是稳定射频,但很快就发现石英晶体也可用于时间测量。1928 年,美国人自豪地展示了世界上第一台石英控制的时钟。
The Tuning Fork Crystal Sets New Precision Standards 音叉晶体树立了新的精度标准
Before this breakthrough, all clocks worked purely mechanical. By installing the quartz crystal and a corresponding energy source that makes the quartz oscillate, an electronic component was introduced for the first time. And it worked: The new quartz watch ran much more precisely than the purely mechanical competition!
在这一技术突破之前,所有时钟都是纯机械工作的。通过安装石英晶体和使石英振荡的相应能源,这是人类首次在时间计量中引入了电子元件。它的确奏效了:新的石英表比纯机械竞争的运行要精确得多!
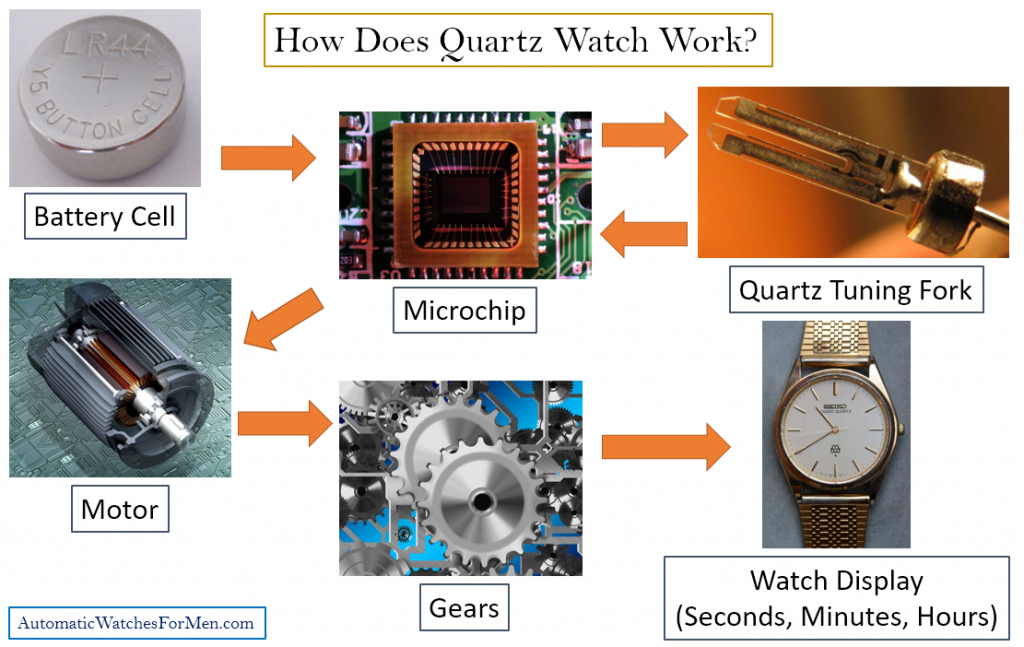
But what function is actually fulfilled by the quartz crystal? Put simply, the quartz crystal ensures that the watch “knows” how long a second lasts. This is achieved by generating a frequency of exactly one Hertz. Hertz is the common unit of measurement for frequencies. It indicates the number of repetitive processes per second in a periodic signal; in this case the advancement of the second hand by one position on the clock-face.
那么,石英晶体到底扮演了什么角色呢?简而言之,石英晶体确保手表“知道”一秒钟的持续时间。这是通过生成恰好 1 赫兹的频率来实现的。赫兹是频率的常用测量单位。它表示周期性信号中每秒重复过程的数量;在这种情况下,秒针在钟面上前进一个位置。
Output Frequency of 32.768 kHz? 输出频率为32.768 kHz?
Where does the unique standard frequency for a tuning fork crystal of 32,768 Hertz originate? To understand this, you must know that the frequency of a quartz crystal depends on its shape and size. A quartz with a natural frequency of only one Hertz would be so large, it would be more suitable for the “Big Ben” clock tower than for a wrist watch. Obviously, that would be rather impractical in terms of production and use so there’s a special trick.
32768 赫兹音叉晶体的独特标准频率从何而来?要理解这一点,您必须知道石英晶体的频率取决于其形状和大小。固有频率只有一赫兹的石英会特别大,它更适合“大本钟”钟楼,而不是手表。显然这在生产和使用方面是相当不切实际的,所以这里有一个特殊的技巧。
Watch crystals with a frequency of 32.768 kHz are relatively easy to produce. Built into the watch, its original frequency is split using so-called T-flipflops . Each T-flip-flop can halve the frequency of the quartz. If 15 of these T-flipflops are connected in series, the output frequency of 32.768 kHz equals exactly one Hertz. Thus, the frequency of the classic Tuning fork crystal is ultimately the result of a simple arithmetic operation and the general conditions of quartz production.
频率为 32.768 kHz 的手表晶体相对容易制造。内置于手表中,其原始频率使用所谓的 T 型进行分割。每个T 型触发可以将石英的频率减半。如果其中15 个T 型触发串联连接,则 32.768 kHz 的输出频率恰好等于 1 赫兹。因此,经典音叉晶体的频率最终是程序运算和石英量产得以简单化的完美结合。
Precise Frequencies for the Mass Market 面向大众市场的精确频率
Several decades passed before the quartz watch finally found its way into the mass market. In 1969, the Japanese company Seiko launched the first commercially available quartz wristwatch on the market. However, the cost of 460,000 Yen was equivalent to that of a small car. But development was rapid: By the mid 1970s, quartz watches were already cheaper than “conventional” watches with purely mechanical movements.
几十年过去了,石英表终于进入大众市场。1969 年,日本精工公司在市场上推出了第一款商用石英腕表。然而,46万日元的成本相当于一辆小型车的成本。但发展很快:到 1970 年代中期,石英表已经比纯机械机芯的“传统”手表便宜。
P.S
In the 1930s, Adolf Scheibe and Udo Adelsberger worked on the construction of quartz clocks at the „Physikalisch-Technische Reichsanstalt“ in Berlin. Quartz Clocks were also popular in the UK, were Louis Essen constructed in 1938 clocks with ring-shaped quartzes at the National Physical Laboratory.
在 1930 年代,Adolf Scheibe 和 Udo Adelsberger 在柏林的“Physikalisch-Technische Reichsanstalt”从事石英钟的制造工作。石英钟在英国也很受欢迎,是 Louis Essen 于 1938 年在国家物理实验室用环形石英建造的钟表。
The first commercially available quartz watch for industry and science was developed by the Physikalisch-Technische Entwicklungslabor Dr. Rohde und Dr. Schwarz (today: Rohde & Schwarz) in Munich. The CFQ quartz watch was launched on the market in 1938.The first wristwatch for the mass market was Seiko’s in 1969.
第一款用于工业和科学的商用石英表由慕尼黑的 Physikalisch-Technische Entwicklungslabor Dr. Rohde und Dr. Schwarz(现:Rohde & Schwarz)开发。CFQ 石英表于 1938 年投放市场。第一款面向大众市场的腕表是 1969 年的精工腕表。




